标签: 链表
难度: Medium
给你一个链表的头节点 head 。
链表中的节点 按顺序 划分成若干 非空 组,这些非空组的长度构成一个自然数序列(1, 2, 3, 4, ...)。一个组的 长度 就是组中分配到的节点数目。换句话说:
- 节点
1分配给第一组 - 节点
2和3分配给第二组 - 节点
4、5和6分配给第三组,以此类推
注意,最后一组的长度可能小于或者等于 1 + 倒数第二组的长度 。
反转 每个 偶数 长度组中的节点,并返回修改后链表的头节点 head 。
示例 1:
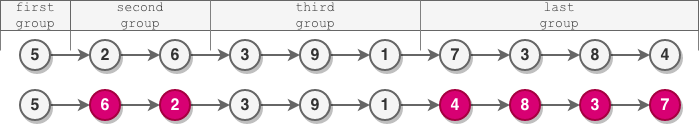
输入:head = [5,2,6,3,9,1,7,3,8,4] 输出:[5,6,2,3,9,1,4,8,3,7] 解释: - 第一组长度为 1 ,奇数,没有发生反转。 - 第二组长度为 2 ,偶数,节点反转。 - 第三组长度为 3 ,奇数,没有发生反转。 - 最后一组长度为 4 ,偶数,节点反转。
示例 2:
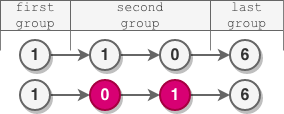
输入:head = [1,1,0,6] 输出:[1,0,1,6] 解释: - 第一组长度为 1 ,没有发生反转。 - 第二组长度为 2 ,节点反转。 - 最后一组长度为 1 ,没有发生反转。
示例 3:
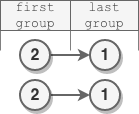
输入:head = [2,1] 输出:[2,1] 解释: - 第一组长度为 1 ,没有发生反转。 - 最后一组长度为 1 ,没有发生反转。
提示:
- 链表中节点数目范围是
[1, 105] 0 <= Node.val <= 105